Perhaps one of the most intriguing phenomena for humanity is why the sky is blue. Even when explained, it’s challenging to imagine that this vibrant color on a sunny day is “just” a composition of lights.
Whether you’re a nature enthusiast or conducting school research, in this guide, you’ll be amazed by the physics behind this wonder that has puzzled us for centuries.
So, continue reading with us in this Insight Factory guide and be enchanted by the explanation behind this celestial marvel, as captivating as the blue sky itself!
Why is the sky blue?
One of the most common questions about nature is why the sky is blue, and the answer is simple but requires a bit of knowledge about physics.
The phenomenon explaining the blue color of the sky is called Rayleigh scattering, discovered by the British physicist John Tyndall in 1871.
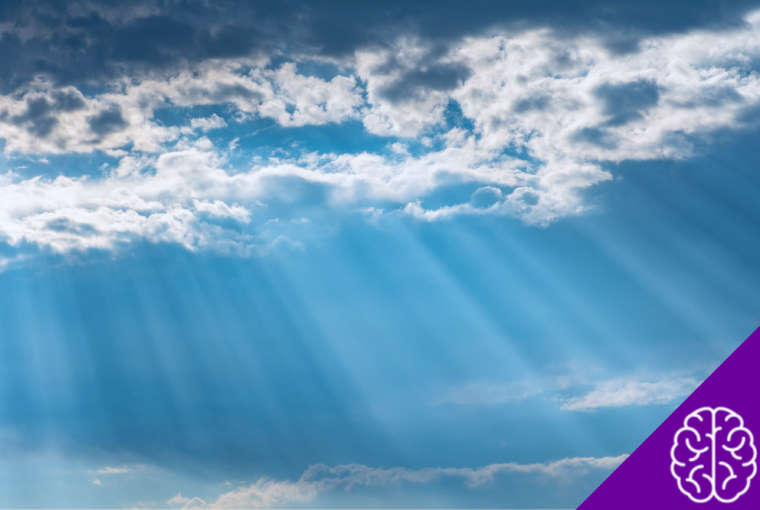
In general, the sky’s color is blue due to an effect related to sunlight. Sunlight consists of all the colors of the rainbow, each with a different wavelength. In other words, the white light emitted by the sun is, in fact, a mixture of colors forming the visible spectrum.
When sunlight reaches Earth’s atmosphere, it is scattered in all directions by gas molecules such as oxygen and nitrogen.
The wavelength of blue light is shorter than that of other rainbow colors, making it more easily scattered by atmospheric molecules. Hence, it is the blue light that we most frequently see, giving the sky its bluish color.
An interesting curiosity about the topic is that the intensity of the blue sky’s color varies with the amount of particles in the atmosphere.
For example, on clear days with few clouds, the sky is bluer because there are fewer particles to scatter the blue light. On cloudy days, the sky is darker as the clouds scatter all rainbow colors.
Moreover, longer colors such as red and orange are less scattered and are more visible during sunrise and sunset when sunlight traverses a greater atmospheric thickness.
Factors like the amount of particles in the atmosphere (such as dust and pollution) and the sun’s position relative to our location can also affect the sky’s appearance.
In more polluted areas, the sky may appear more gray due to particle scattering instead of the clear and dazzling blue.
And what is the explanation for the color of the sky at night?
We’ve discussed the sky’s color during the day and the beautiful sunrise and sunset, but what about the strong blue color we see in the night sky? Well, the nighttime scene reveals a different palette due to a combination of two factors.
At night, starlight and moonlight, combined with the lack of direct sunlight, make the sky take on darker tones, often appearing in shades of black, dark blue, and purple.
Interesting facts about the sky’s color:
- On other planets, the sky may have different colors. For instance, on Mars, the sky appears reddish due to a high concentration of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere
- The sky may seem bluer at higher altitudes because the thinner atmosphere at greater heights scatters blue light less
- The location on Earth also affects the sky’s color. Near the poles, the sky may appear lighter due to the angle at which sunlight reaches the atmosphere, while near the equator, the blue may seem more intense
Did you like to know about the topic?
Liked learning about the topic? We hope to have clarified for you why the sky is blue, satisfying your curiosity.
So, the next time you gaze at the sky, remember the science behind its blueness, all a result of the complex interaction between sunlight and atmospheric molecules.
This is truly a fascinating phenomenon that reminds us of the beauty and complexity of our universe. Enjoy!